What’s the Big Idea?
IT Solution Design a Guide to Creating High-Quality IT Solutions In today’s digital age, industries depend completely on IT services in order to stay competitive, achieve operational efficiency, and satisfy their customer requirements.
Designing IT solutions in line with business requirements has become a necessity with the evolving technology. The design of the IT solution is what makes for efficient, secure, and scalable systems that provide value to a business and its customers.
In this definitive guide, we’ll take an in-depth look at what IT solution design is, why it’s of value, the process for developing an IT solution, and the pros and cons of this design process.
What is IT Solution Design?
IT Solution Design is the strategic process of designing, delivering, and supporting IT (Information Technology) solutions to fulfill business and user requirements.
It involves: assessing the needs of an organization, designing a concept that will meet these needs, and developing a blueprint on how technology can be put to use in order for business processes to run smoothly.
Design of IT solutions is crucial in developing systems that are functional as well as scalable and secure. It specializes in getting technology to work with business processes while doing so efficiently, all the while providing a seamless experience for internal teams as well as external customers.
The essence of IT solution design comprises various fundamental elements:
- Requirement Gathering: Analyzing business needs and goals.
- System Architecture: Defining hardware, software, networking, and security details of the solution.
- Integration: Integrating IT solutions into current systems and data sources.
- Realization: Constructing the solution based on the design.
- Testing and Validation: Confirming the solution has been built correctly and does what’s expected.
Why is IT Solution Design Important?
IT solution design is important because it provides evidence that an IT system is in line with the business requirements and conditions. A good IT solution can bring its fair share of advantages:
Streamlining Operations
By automating processes, integrating systems, and improving communication across the organization, IT solutions enable companies to run more efficiently.
Scalability
A good IT architecture is built in a way that allows the solution to scale with the business and meet its needs as it grows.
Security
As data privacy issues and cybercrimes have been on the rise, security is becoming a part of IT solution design to protect the integrity of data and the system.
Cost Efficiency
Well-designed business packages also prevent businesses from overspending on what has been budgeted because no unnecessary features or resources will be part of a solution.
Enhanced Decision Making
IT solutions help organizations in collecting critical information that can be used to make choices and thereby take better business decisions. IT solution design is the foundation of an effective IT system that drives business growth, operational efficiency, and customer service.
A reckless lack of a design phase ensures that companies struggle through requirements for technology to be built that they don’t truly need – it’s not hard to see the financial waste, inefficiencies, and potential security breaches this allows.
Critical Phases for IT Solution Design
The design process of an IT solution consists of multiple phases, ranging from understanding business requirements to deployment and testing of solutions. Here are the major steps involved:
Identifying Business Requirements
Before you can start the design of an IT solution, it is important to understand what those business needs of your organization are. This phase involves:
- Working with Key Stakeholders: Business leaders, department heads, and end-users must define requirements based on specific challenges or goals.
- Business Objectives: Precisely defining what the IT solution needs to accomplish (i.e., improve customer experience, lower costs, make business operations more efficient).
- Review of Current Systems: Review current operations to identify areas that need to be added or improved.
- Defining Functional and Non-Functional Requirements: Functional requirements describe the specific features or functions a system should possess, whereas non-functional requirements deal with how well the system performs (e.g., scalability, reliability, security).
After the business requirements are defined, these need to be detailed for all people involved to have a clear understanding of what should be produced by the IT solution.
Conceptual Design
After addressing the ‘what’ problem, the next step is to visualize the IT solution. This stage includes the design of the overall high-level structure and system. This phase is characterized by:
- System Architecture: This defines how the system and its components interact with one another, including databases, application servers, user interfaces, or networking infrastructure.
- Data Flow Design: Understanding how information travels through the system, from data input and processing to output. This can be portrayed using data flow diagrams or system flow charts.
- Integration Points: Determine which systems will need to integrate with the new solution, such as legacy systems, third-party products, or cloud services.
The concept design is a blueprint for the detailed system architecture and influences the IT solution development.
System Architecture Design
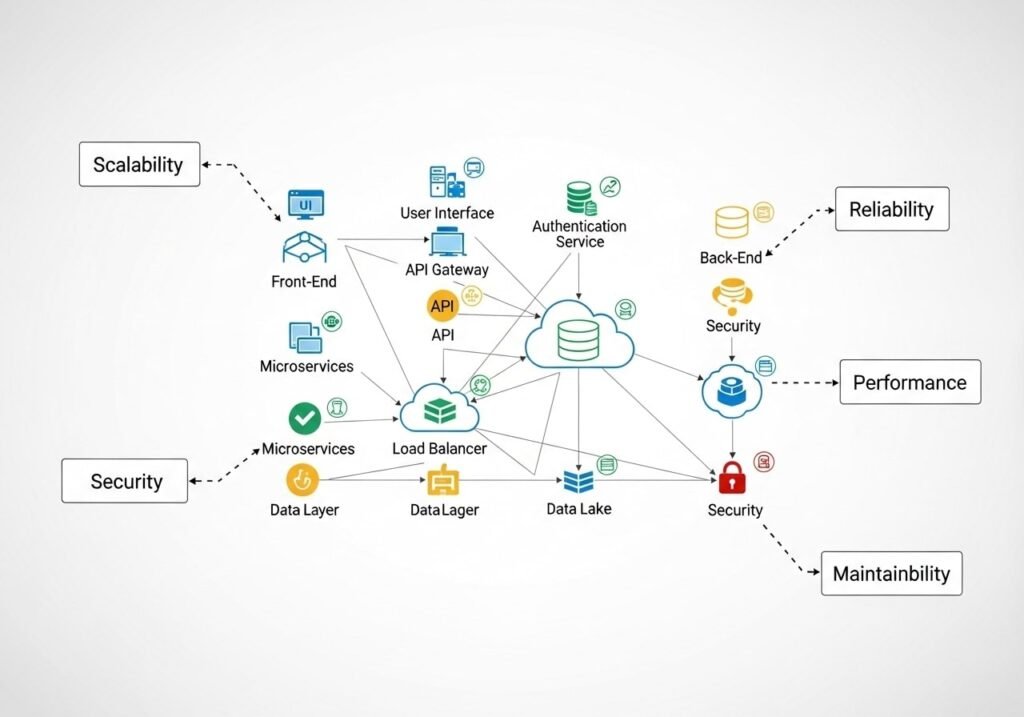
Once the high-level design is complete, the next step is system architecture design. This phase focuses on the technical details and structure that will support the IT solution. Key considerations include:
- Hardware Requirements: Identifying the hardware, including servers, storage, and network devices.
- Software Choices: Determining which software systems, frameworks, or tools will be used to develop the system.
- Hardware Infrastructure: Creating a system architecture, such as local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and cloud services.
- Safety Protocols: Ensuring the solution is developed with safety features such as encryption, firewalls, and user access controls.
This is where the technological underpinnings of an IT solution are established, laying down the foundation for development.
Data Design
Data is at the heart of any IT solution, and how that data is managed or processed informs part of the initial design. The data design process includes:
- Database Design: Structuring how data is stored, retrieved, and managed in the database. The database should facilitate business processes and be accessible for easy retrieval of information and analysis.
- Data Communication: Data should be able to move freely within the system. This also covers how data is acquired, analyzed, retained, and shared.
- Data Integration: The IT solution may need to coexist with other data sources or systems. Planning for compatibility and data integrity is critical.
- Data Security: Ensuring that sensitive information is secure from unwanted access is essential for data design.
A sound data design allows the system to handle business needs effectively, both now and in the future.
Integration Design
Today, IT solutions are usually required to interact with other systems, inside and outside the company. The integration design phase ensures that the new solution can be integrated with any tools, systems, and data sources already in use.
Integration design covers the following aspects:
- API Development: Creating APIs that allow different systems to interact with each other and share data.
- Middleware: Software that connects different applications or services to facilitate integration between them.
- Data Synchronization: Ensuring data is integrated between systems and remains coherent.
- Third-Party Integration: In many cases, the IT solution will need to interact with third-party applications and services. Understanding how that works and ensuring it is secure and reliable is crucial.
Integration design ensures the IT solution functions well within the organization’s entire system.
Testing and Validation
Once the solution has been designed and created, it needs to be tested to verify its correct operation. The testing stage includes:
- Functional Testing: Ensuring that all features and operations work according to requirements.
- Performance Testing: Verifying that the system can handle the expected load and will work under high-traffic conditions or intensive use.
- Security Testing: Checking for potential vulnerabilities and making sure the solution is resistant to cyber threats.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Involving end-users in testing to ensure the solution meets their needs and is user-friendly.
This stage of the project ensures the solution is robust, reliable, secure, and ready for deployment.
Deployment and Monitoring
After the IT solution passes testing, it is ready to be deployed. This stage includes deploying the solution and monitoring it after it goes live to solve any arising problems. Key activities include:
- System Monitoring: Monitoring solution performance, security, and user activity to ensure its overall effectiveness.
- Maintenance and Support: Supporting users on an ongoing basis and maintaining the system to ensure it remains secure and up-to-date.
Benefits of IT Solution Design
The effects of IT solution design are unique and stand both in terms of business process operations and technology. These benefits include:
- Better Productivity: Improve efficiency and eliminate manual work by automating procedures and integrating systems.
- Closer Match with Business Processes: The IT solution is adapted to the needs of the company and business goals.
- Scalability: Once the system is well-designed and maintained, it can adjust to new users, data, or functions with ease without fundamental design changes.
- Better Security: Security is incorporated into the architecture, safeguarding confidential data and preserving the integrity of users in the system.
- Cost Savings: By focusing on the essentials and improving system design, companies can save money by not purchasing unnecessary resources and features.
Challenges in IT Solution Design
While IT solution design offers numerous benefits, it also poses several challenges:
- Complexity: Designing IT solutions to meet the complex nature of business operations and integrating them with existing applications can be difficult.
- Budget: Finding the balance between development costs and quality design can be challenging, especially for small to medium-sized companies.
- Time: Designing and developing a comprehensive IT solution takes time, but most businesses are constantly pushed to stay on track with deadlines.
- Resistance to Change: Employees and stakeholders may resist bringing in new technology, especially if they are unfamiliar with it or have not received adequate training.
Conclusion
In short, IT solution design is a key component of any business technology strategy. By taking a methodological approach, from analyzing business needs to testing and implementation, organizations can create IT solutions that are cost-effective, scalable, and secure—meeting the goals of their business. A well-thought-out IT solution can automate, optimize, and prepare an organization for success.
FAQs
Q1: What is IT Solution Design?
IT solution design refers to the processes involved in developing and configuring technology systems to meet business requirements.
Q2: What is the importance of IT solution design?
It enables technology solutions that are conducive to business objectives in terms of efficiency, scalability, and security.
Q3: What are the critical aspects of IT solution design?
Key steps include defining business requirements, modeling the design, creating system architecture, developing data strategies, ensuring integration, and finally, testing and deployment.
Q4: Why is IT solution design important?
Advantages include increased efficiency, closer alignment with business objectives, scalability, security, and cost savings.
Q5: What are the challenges in IT solution design?
Challenges include complexity, resource limitations (fiscal, time), and stakeholder resistance to change.
Q6: How can companies deal with challenges in IT solution design?
Businesses can face these issues with advanced planning, early engagement of stakeholders, investment in training, and the use of skilled IT professionals.